Likelihood to Engage helps marketers to better understand and act on customer engagement patterns. Marketers can use this feature to:
-
Monitor the health of their audience by counting users in each engagement group
-
Proactively reach out to customers who are likely to churn with re-engagement campaigns
-
Delight top customers with special offers or rewards to reinforce loyalty
You can also watch this video which explains this feature.
What is Likelihood to Engage?
The Likelihood to Engage feature in Cheetah Digital is based on an ML Score from the Machine Learning Engage (ML Engage) model that utilizes customers' engagement data from Marigold AI Profile. The Likelihood to Engage ML score, which has a value of High/Medium/Low reflects each user’s likelihood to engage with future marketing efforts. This score is generated based on key behavioral signals, including email opens, clicks, unsubscribes, spam complaints, and web conversion events.The ML score is updated in the AI Profile table in Cheetah Digital when synced. This table can be joined to the customer table, so it can be used for segmenting subscribers and dynamic content development.
With the Likelihood to Engage model running weekly, marketing teams gain timely insights to make smarter, data-driven decisions that boost engagement and retention.
What is a Control Group?
A control group is a subset of users excluded from model-driven decisions to serve as a baseline for comparison. It helps measure the true impact of the model by showing how users behave without model interventions.
Marigold AI models maintain a control group consisting of a random selection of your recipients. This control group serves as a baseline, allowing you to measure the model's impact by comparing results against users who were not influenced by the model. The control group is static, meaning once a recipient is selected into the control group, they remain in it. This consistency ensures accurate comparisons over time.
Who are Unscored Users?
Some users may remain unscored by the model because there isn't enough behavioral data collected about them. Without sufficient data (e.g., opens, clicks, purchases), the model cannot predict outcomes for these users.
An example of an unscored user is a new subscriber, as the model does not yet have sufficient data about their behavior. Another example is an inactive user who hasn't engaged with the platform recently, resulting in limited behavioral signals for the model to analyze.
How to Request Likelihood to Engage
Likelihood to Engage is an optional feature that must be enabled in your account. Please speak with your Marigold Representative for more details. You must also have Personalized Send Time enabled in your account to use Likelihood to Engage.
How to use Likelihood to Engage
When Marigold AI (Personalized Send Time and Likelihood to Engage) is enabled for your organization, you will be presented with the Machine Learning Recipient Table in Cheetah Digital.
The AI profile attributes from the Machine Learning Recipient Table can be used in filters for segmentation purposes through Cheetah Digital Table Join.
Using Likelihood to Engage in Email Campaigns involves the following steps.
-
Define Joins for your customer tables to the Machine Learning Recipient Table
-
Create Filters
-
Use the filters in Cells and Splits campaigns and create Dynamic Blocks to use in Email Campaigns
Define Joins to the Machine Learning Recipient Table
The Machine Learning Recipient Table can be joined to the customer’s tables using two different types of joins:
Property join: is a "one-off" join method used in creating filter logic, and is not a permanent join.
Entity join: can only be defined by a Marigold admin. This is a more permanent join method, as these joins cannot be deleted once defined. Please contact your Marigold Representative to assist you in setting up entity joins for your tables. Entity joins are usually work faster than property joins, when implemented.
Property Join
When the ML models for Personalized Send Time and Likelihood to Engage are enabled in your account, the Machine Learning Recipient table will be available in the filter for property-to-property join via a common field - email address.
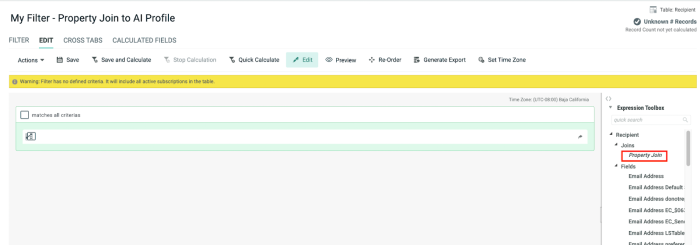
To join the current table to the Machine Learning Recipient (AI Profile) Table, from the Expression Toolbox in the right pane, select the customer table (Recipient table in the above example) > Joins > Property join, then drag and drop the Property Join to the Filter.
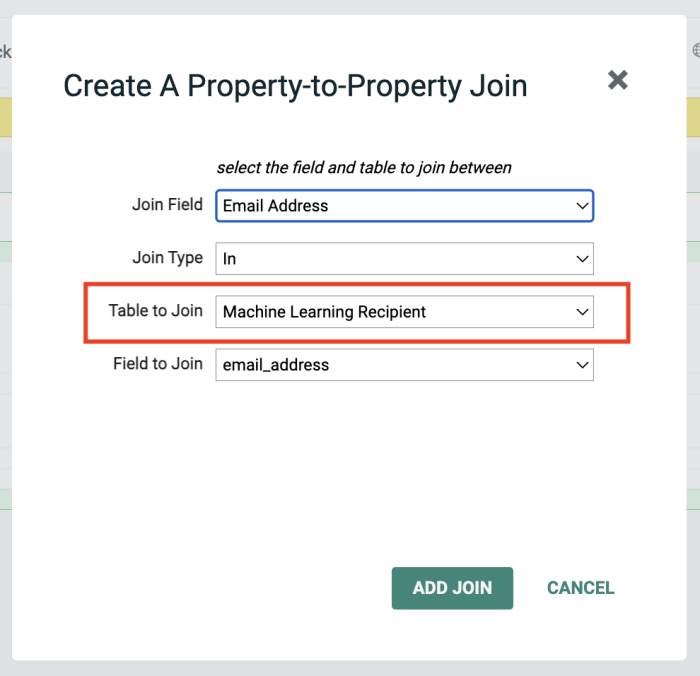
In the displayed popup window enter select “email_address” as the field to join and Machine Learning Recipient as the Table to Join.
Click Add Join.
When a property join is defined in a filter, you can use the Machine Learning Recipient attributes for segmentation.
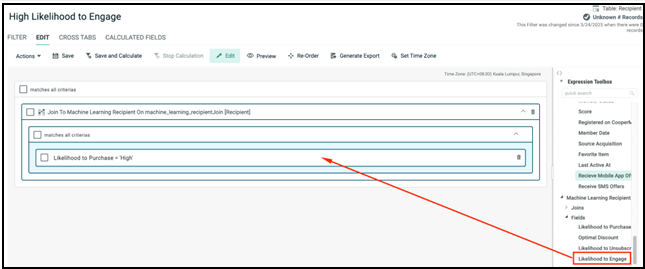
To target the audience based on their likelihood to engage, you can create various filters with Likelihood to Engage as filter criteria with options High, Medium and Low.
Filter criteria - Likelihood to Engage contains “High”
Entity Join
When the ML models for Personalized Send Time and Likelihood to Engage are enabled in your account, the Machine Learning Recipient Table will be available in the filter for entity joins.
In order to create entity joins contact your Marigold Representative.
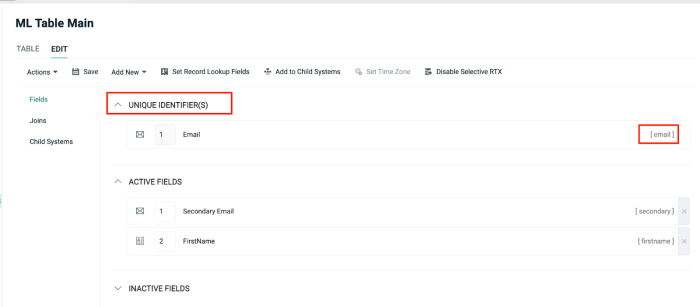
To join the Customer Table and the Machine Learning Recipient Table on the email field, the email field must be a unique identifier in the Customer Table, as shown in the example below:
Please Note:
1. Only one join is allowed for each entity table.
2. For an entity table with email as the unique identifier, the system will join it automatically. However, the user is also given an option to define a soft match using a different email field from 24.7.0.
3. We recommend adding Entity Join to tables that are frequently used. Adding joins to all tables could adversely affect import performance.
Entity tables typically have a large data size. The import performance may be affected as adding a new entity join will affect the other entity tables.
4. Joins that are added cannot be deleted. They will remain visible in Cheetah Digital such as in Filters, even when the ML Engage model is disabled.
5. When ML Engage model is disabled after it was activated, new ML data related to the User Engagement will not be synced from the ML to Cheetah Digital.
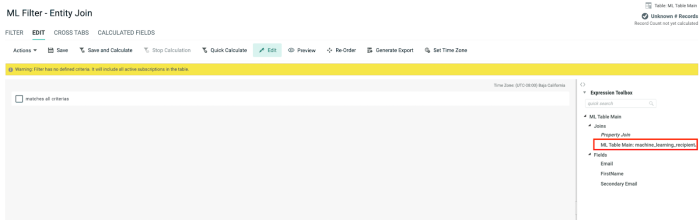
When entity join is set in your Cheetah Digital account, the Machine Learning Recipient table associated with the source table will be listed for selection in the Filter (under Join), allowing you to add a field from the joined Machine Learning Recipient table as a selection criterion similar to the property-to-property join explained above.
Filters
Whether you're using entity or property join, we recommend the creation of four reusable filters using the “Likelihood to Engage” field with score values of High, Medium, Low and NULL as below:
-
Filter 1: Likelihood to Engage is High
-
Filter 2: Likelihood to Engage is Medium
-
Filter 3: Likelihood to Engage is Low
-
Filter 4: Likelihood to Engage is Null
Once created, these filters can be used to render different contents or discounts in Dynamic Blocks and Cells & Splits campaign.
When these filters are created, they can be used to target various groups of audience. For example:
-
Email a coupon to customers with a High Likelihood to Engage score to improve engagement.
-
Send a "surprise and delight" email to customers with a Low Likelihood to Engage score, to re-engage them and reduce opt-out.
Additionally, they can be used to differentiate content between "high," "medium," and "low" score values using dynamic blocks or split cells campaign within a single campaign.
For customers with no score (NULL), which means there was not enough data to score them, we suggest using your best practice or preferred discount.
Using Pre-defined Filters in Dynamic Block and Cells and Splits Campaign
Dynamic Block
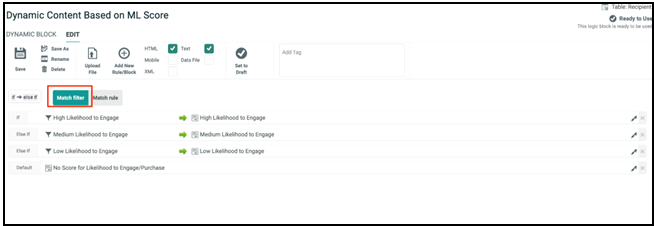
Cheetah Digital provides two different methods for marketers to enable different recipient groups to get content variation; they are by filter (Match Filter) and by a value in a field (Match Rule).
To use the filters created in the above section in a dynamic block, use the Match Filter option. This enables you to apply the filters based on discount values and break the campaign audience into smaller, unique groups, so each of these can receive unique content or offers.
You can now insert the above created dynamic block in your email campaign.
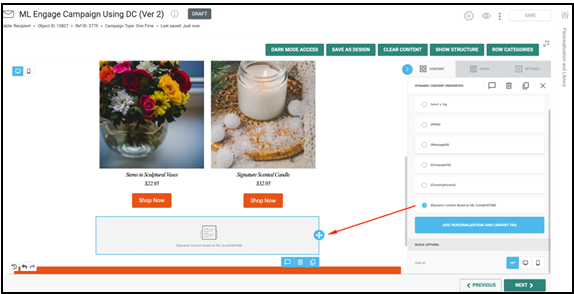
Below is a sample campaign using a dynamic block based on the different ML engagement scores, demonstrating how the ML model can be used to target various audience groups to improve engagement.
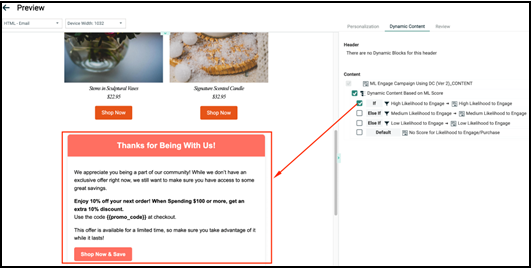
Dynamic content for subscribers who meet the 'Likelihood to Engage = High' filter criteria.
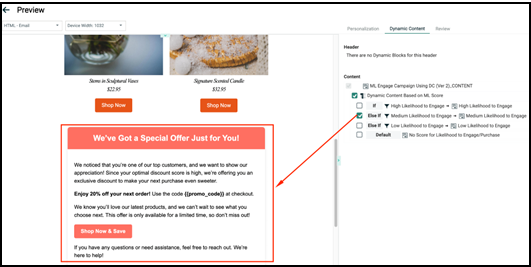
Dynamic content for subscribers who meet the "Likelihood to Engage = Medium" filter criteria.
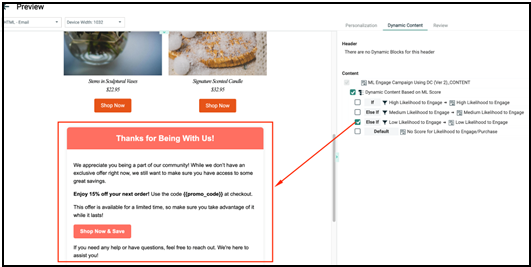
Dynamic content for subscribers who meet the "Likelihood to Engage = Low" filter criteria.
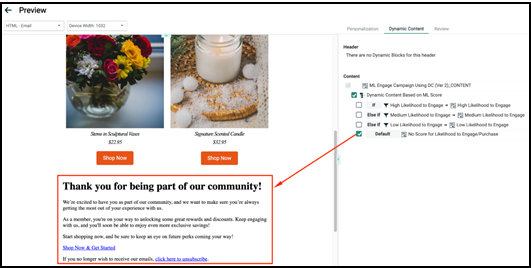
This is the default content for subscribers who do not have a score for “Likelihood to Engage”.
Split cells campaign
To use the filters created in the above section in a Split Cells Campaign, split the campaign by filter. This enables you to use the Filter to define the Audience for each sub-cell as shown in the screenshots below.
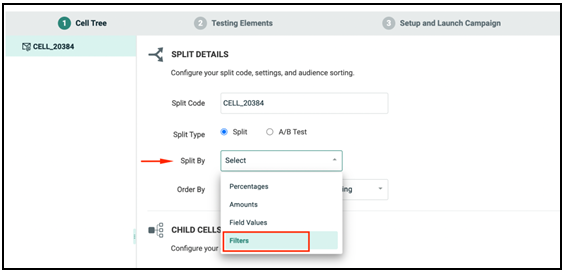
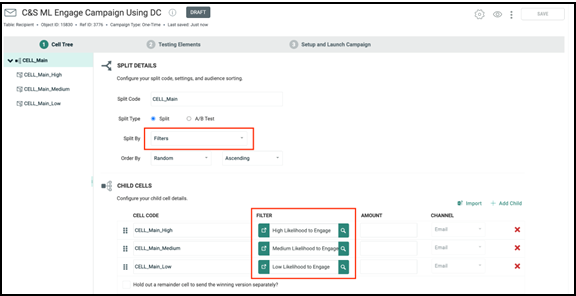
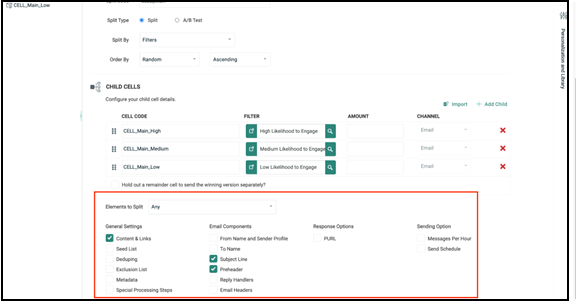
Note: By enabling the Content & Links, Subject Line, and Preheader as test elements of a Split Cells campaign, you can create different content variants for the various audience groups.
Machine Learning Recipient Attributes
Once the Joins are created with the Machine Learning Recipient table, the following attributes are available for Segmentation:
| Field | Sample Values | Description | Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Likelihood to Engage | [High,Medium,Low] | Likelihood to engage (or continue engaging) with the brand in the next 4 weeks | ML Engage |