Journey scheduling
Schedule the execution of the journey and define the start and end date of the journey. If no scheduling is defined the journey is executed the moment it is launched. This is the same as a single shot journey without a start date.
There are three ways of scheduling the execution:
Single Shot
A single shot journey is executed once and automatically put on hold after execution. A typical example is a newsletter that is sent once to all contacts in the audience. Newsletters and other mailings that are sent once to all contacts are typical examples of a single shot journey.
For a single shot journey flag the corresponding option and set a start date.
When the start date is reached, the journey is executed. If no start date is set, the journey is executed immediately when launched.
Note: Emails are sent only once to the same contact. If you would reactivate the journey again, the contacts that already received the email, will not receive it a second time. The opt-out value for the contact is also taken into account. If the contact is opted out (OPTOUT field > 0) the contact will not receive the email, even if he is in the target selection of the journey .
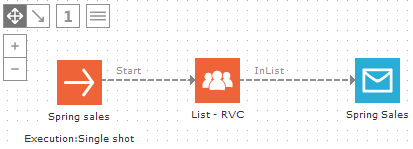
A typical example of a single shot email journey, with an Audience and an Email component:
Data Driven
A data driven journey is executed at a certain time interval. The execution can be scheduled once a week, daily, hourly or following a custom setting. By default the journey is executed every ten minutes. Each execution interval the target audience is checked based on the filter criteria (with the Filter Designer) defined in the audience list segment or in the Audience component properties. So each interval the target audience can be different. Contacts that are in target at that moment, but already had the message sent, will not it be targeted again. Only new contacts at that execution interval will have the message sent.
Example: A scheduled journey sending a welcome message to new contacts every ten minutes. Every ten minutes the target is checked for new contacts, who did not had the message sent. Everyone who already had the message sent will not be included in the target. This journey does not have a start and end date and runs forever, immediately when launched.
Example: A segment 'Birthday' contains contacts in the Audience list that have their birthday today. The segment is selected as an audience in the journey. Only contacts that fall in the segment at the execution interval will get a birthday message. So every day contacts are added to and removed from that segment. Selligent detects them and sends them the message. This means this journey works for one year. Next year, when it is the contacts birthday again, he will not receive the message again, because he already received it the previous year. Each year the journey has to be duplicated. Alternatively, you can create a triggered journey or a BPM journey.
Note: The opt-out value for the contact is also taken into account. If the contact is opted out (OPTOUT field > 0) the contact will not receive the email, even if he is in the target selection of the journey .
Note2: Data driven journeys in combination with action lists can send the same message multiple times to the same contact. See action lists and the Basket abandon example.
Triggered
A ‘Triggered’ journey is executed on a predefined moment in time. The execution is not limited to a fixed interval (e.g. every two days, twice a week, etc) but can be irregular and at any given moment in time. (e.g. 18/10/2014 at 10:00, 23/10 at 17h, etc). There is no limit to the number of triggers that can be defined.
The same message can be sent multiple times to the same contact, something that is not possible with a single shot or data driven journey.
Example:
An event for which you have to send out the same reminder message once a week, for three weeks, to the contacts in the audience. This means that contacts will get the same message week after week as long as the journey is active. Since the journey only needs three triggers, they can easily be defined in the journey properties.
Emails can be sent multiple times to the same contact. When the journey is set to 'Triggered', in the properties of the Email component, check 'Allow this email to be sent multiple times to the same contact'. The Email component icon will change.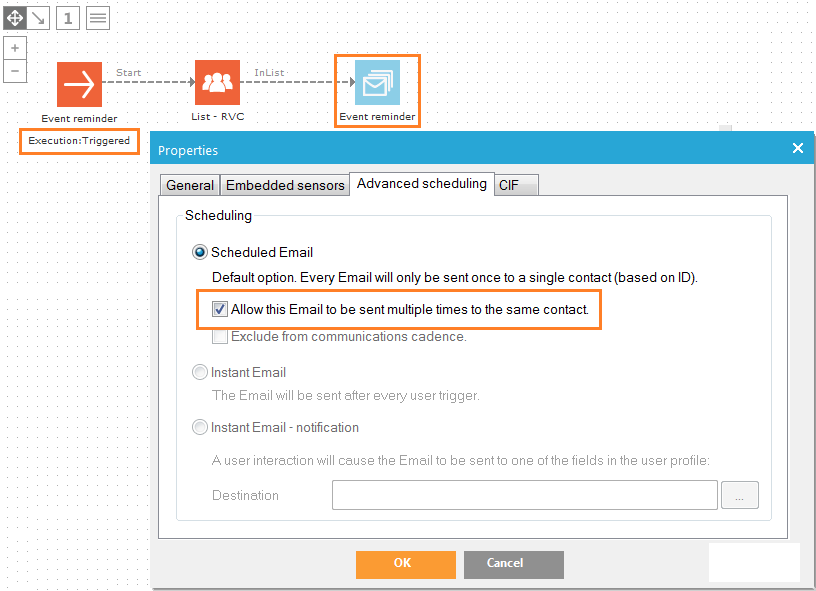
The opt-out value is taken into account. If the contact is opted out (OPTOUT field > 0) the contact will not receive the email, even if he is in the target selection of the journey .
Triggers can be defined manually, but an SQL statement can be created as well to generate triggers.
A: Manually
To manually define a trigger, select the option 'Triggered' and press the 'Schedule' button. The ‘journey triggers’ page is displayed:
The table displays an overview of the triggers that have been defined for the current journey. Press the 'Add' button to create new triggers:
On the 'Properties' tab following options are defined:
- Activation date and time: the date and time on which the journey must be executed
- Enabled: several triggers can be defined for one and the same journey. These do not all have to be enabled at once. The option ‘enabled’ allows activating or deactivating triggers.
- Confirmation required before mails are sent: it is possible to request a confirmation before mails are send out. This option can be used when the journey is still in testing phase.
Example: if the message must be sent every Monday morning at 8 am, triggers need to be created with the date and time of every Monday on which the message is sent out.
B: SQL Statement
Technical note:
The table storing the triggers is 'CAMPAIGNTRIGGERFLAGS'. Fields that need to be set are CAMPAIGNID (=journey id), START_DT (=start date), ENABLED (=1 if enabled), REQCONFIRM (=1 if confirmation required. Confirmation must be handled manually, no automated way is defined in Selligent Campaign for confirmation before sending), STATE should be 0 (the trigger won't work when the state is empty/null).
Start and End Date
For each scheduling, A start and end date can be defined. The journey is active within this indicated period of time.
Once an end-date has been defined the options 'Offline' and 'Hold' at the bottom are enabled. This changes the status of the journey when the end date has been reached.
When a journey is put offline a redirect can be defined. Selligent allows three distinct types of redirects:
- Redirect to an external location: this corresponds to a website The exact URL of this site is entered.
- Redirect to an alternative micro-web. In this case the contact is redirected to a Selligent page. This page is not integrated in a journey.
Press the […] button to access the dialog from which a page can be selected. The tree view displayed in this dialog is the same as in the Selligent Editor. - Use an alternative page from a different journey. In this case a redirect is done to a page in another journey.Press the […] button to access the dialog from which a journey page can be selected.
Action Driven
Apart from these three scheduling types, it is also possible to execute action-driven journeys. An example is a transactional email. Each time the contact does something (action), an email needs to be sent. E.g. the contact orders an item, abandons his basket, does not pay his invoice on time, etc.

